Aplastic anemia
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

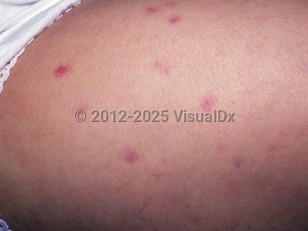
AA presents with pancytopenia, and bone marrow biopsy will reveal hypocellularity. It can be caused most commonly by autoimmune processes, direct injury to the bone marrow (toxic effect, drugs, radiation, etc), viral infection (eg, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, Epstein-Barr, cytomegalovirus, parvovirus B19, HIV), clonal disorders (eg, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, myelodysplastic syndrome, acute myeloid leukemia), or genetic disorders (eg, Fanconi anemia, Shwachman-Diamond syndrome, thrombopoietin abnormalities, telomere abnormalities). Despite the various pathophysiologic mechanisms that can lead to AA, the disorder remains rare, with an incidence in the Western world of 2 per million per year, with half of all cases occurring before the age of 30 years.
Patients with AA usually present with recurrent infections due to neutropenia, mucosal hemorrhage or menorrhagia due to thrombocytopenia, and fatigue, dyspnea, and cardiopulmonary compromise due to anemia.
Codes
D61.9 – Aplastic anemia, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
306058006 – Aplastic Anemia
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:08/18/2024