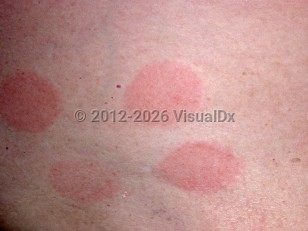
Allergic contact dermatitis
See also in: Cellulitis DDx,External and Internal Eye,Anogenital,Hair and Scalp,Nail and Distal Digit,Oral Mucosal LesionAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a delayed-type (type IV) hypersensitivity reaction that occurs when allergens activate antigen-specific T cells in a sensitized individual. It typically requires repeated exposures before an allergic response is noted and most commonly occurs 24-48 hours after exposure to the offending agent.
Contact dermatitis generally presents with well-demarcated borders, suggestive of an "outside job" or external contact. Causative allergens and their clinical importance vary based on several factors, including exposures based on geographic regions, cultural practices, personal care product usage, and manufacturing practices (eg, which preservatives are used).
Common contact allergens are urushiol (poison ivy, oak, and sumac), nickel, fragrance, cobalt, chromates (leather products), neomycin, thimerosal (ophthalmic preparations and vaccines), adhesives, and oxybenzone (sunscreens). Formaldehyde-releasing preservatives in polypropylene surgical masks have been reported to cause ACD.
Other allergens include epoxy resins (previously recognized for occupational exposure but now also commonly used in recreational activities and hobbies), essential oils (due to terpenes), methylisothiazolinone (a preservative in cosmetics and household products), and (meth)acrylates (nail cosmetics).
Contact allergens may be airborne, such as from cement dust, sprays, or room fresheners, for example (airborne contact dermatitis).
Photoallergic contact dermatitis is contact dermatitis to an allergen that is incited by sun exposure. In North America, sunscreens are the most common photoallergen.
ACD can present as a systemic contact reaction with widespread lesions when the offending agent is ingested, present in an implanted device, or used in a manner that covers a large portion of the body (eg, body washes). Baboon syndrome (symmetric, sharply demarcated erythema of the gluteal or inguinal area as well as other intertriginous or flexural sites) has also been reported as a presentation of systemic ACD.
To raise awareness of increasingly common or problematic allergens, the American Contact Dermatitis Society selects an Allergen of the Year. Recent examples include toluene-2,5-diamine sulfate (PTDS) (2025), sulfites (2024), lanolin (2023), and aluminum (2022).
Related topic: hand dermatitis, irritant contact dermatitis
Codes
L23.9 – Allergic contact dermatitis, unspecified cause
SNOMEDCT:
40275004 – Contact dermatitis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:08/10/2025
 Patient Information for Allergic contact dermatitis
Patient Information for Allergic contact dermatitis - Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient