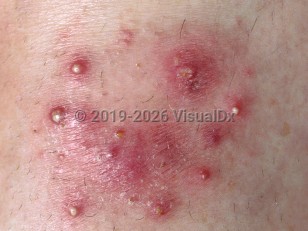
Majocchi granuloma in Adult
See also in: Cellulitis DDxAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Majocchi granuloma can occur following trauma to the skin or from occlusion of hair follicles, such as from shaving the legs or face. Involvement of the buttocks and genital skin has been reported. The use of topical steroids on unsuspected tinea infections and immunosuppressed states can also predispose to its development.
This condition is most common in adults between 20 and 35 years old, with a predilection for females. Majocchi granuloma is more common in females who frequently shave their legs and in those with tinea pedis or onychomycosis.
Immunocompromised patient considerations:
In transplant patients and immunocompromised patients, there is a potential for systemic dissemination. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected individuals with tinea pedis may have a higher risk of progression to Majocchi granuloma on the feet and lower legs.
Majocchi-like granulomas, deep dermatophytosis, severe tinea capitis and corporis, and fungal nail involvement are characteristic of an inherited deficiency of CARD9 (caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 9), an inflammatory cascade-associated protein.
Codes
B35.8 – Other dermatophytoses
SNOMEDCT:
214600002 – Tinea profunda
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:02/26/2025