Emergency: requires immediate attention
Coarctation of the aorta
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

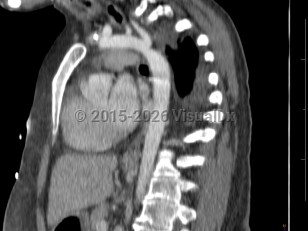
Narrowing of the descending aorta distal to the take-off of the great vessels. Posterior costal arteries and internal mammary and scapular arteries provide collateral flow to the descending aorta. Usually congenital, although can be acquired as a consequence of inflammatory diseases affecting the aorta (eg, Takayasu arteritis). Clinical manifestations vary by age and associated cardiac defects, which may include bicuspid aortic valve, atrial septal defect (ASD), ventricular septal defect (VSD), patent ductus arteriosus, and D-transposition of the great vessels.
Aortic coarctation accounts for 5%-8% of all congenital heart defects and may occur as an isolated defect or in combination with ventricular septal defect and bicuspid aortic valve. Infants typically present with signs of heart failure as the ductus arteriosus closes due to significant increase in afterload with left ventricular strain and pulmonary congestion.
Previously undiagnosed children and adults typically present with hypertension. Systolic pressures are usually higher in the upper extremities than in the lower extremities. Femoral pulses are usually diminished or delayed. Lower extremity claudication occurs with exertion. Lower extremity systolic pressures may be unobtainable.
Aortic coarctation accounts for 5%-8% of all congenital heart defects and may occur as an isolated defect or in combination with ventricular septal defect and bicuspid aortic valve. Infants typically present with signs of heart failure as the ductus arteriosus closes due to significant increase in afterload with left ventricular strain and pulmonary congestion.
Previously undiagnosed children and adults typically present with hypertension. Systolic pressures are usually higher in the upper extremities than in the lower extremities. Femoral pulses are usually diminished or delayed. Lower extremity claudication occurs with exertion. Lower extremity systolic pressures may be unobtainable.
Codes
ICD10CM:
Q25.1 – Coarctation of aorta
SNOMEDCT:
7305005 – Coarctation of the Aorta
Q25.1 – Coarctation of aorta
SNOMEDCT:
7305005 – Coarctation of the Aorta
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:01/12/2022
Emergency: requires immediate attention
Coarctation of the aorta