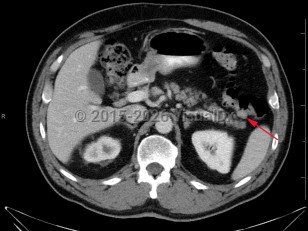
Colonic polyps
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Histologically, polyps may be tubular, villous, or tubulovillous. Villous adenomas are 3 times more likely to become malignant than tubular polyps. The likelihood that a polyp contains invasive cancer increases with the size of the polyp. Most polyps remain asymptomatic and are detected during routine screening colonoscopy. Less than 5% of polyps lead to bleeding.
Once an adenomatous polyp has been detected, the entire colon should undergo surveillance for polyp detection. Colonoscopy should be repeated based on the number and histology of previously discovered polyps. Family history and certain disease processes (eg, ulcerative colitis, familial adenomatous polyposis) can impact surveillance colonoscopy recommendations as well.
Codes
K63.5 – Polyp of colon
SNOMEDCT:
68496003 – Polyp of colon
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:04/19/2017