Perichondritis
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

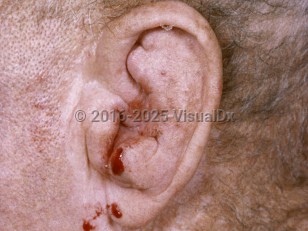
Perichondritis is an infection of the soft tissue that encloses the auricular (ear) cartilage. It typically presents with erythema, edema, and tenderness in the pinna of the ear. Infection is usually bacterial, introduced through local trauma (ie, piercing) or burns. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus are the bacteria most commonly implicated, and polymicrobial infection is common. Immunocompromised patients are at increased risk for perichondritis. Perichondritis can be the presenting infection of human immunodeficiency virus, lymphoma, and, in some instances, diabetes mellitus.
Relapsing polychondritis is a rare noninfectious disorder that mimics perichondritis.
Perichondritis is treated with systemic antibiotics that include both pseudomonal and staphylococcal coverage. If untreated, infection may spread into the deeper cartilage of the ear (chondritis), causing more significant injury.
Relapsing polychondritis is a rare noninfectious disorder that mimics perichondritis.
Perichondritis is treated with systemic antibiotics that include both pseudomonal and staphylococcal coverage. If untreated, infection may spread into the deeper cartilage of the ear (chondritis), causing more significant injury.
Codes
ICD10CM:
H61.009 – Unspecified perichondritis of external ear, unspecified ear
SNOMEDCT:
37600001 – Perichondritis
H61.009 – Unspecified perichondritis of external ear, unspecified ear
SNOMEDCT:
37600001 – Perichondritis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:03/28/2019
Last Updated:03/28/2019
Last Updated:03/28/2019
Perichondritis