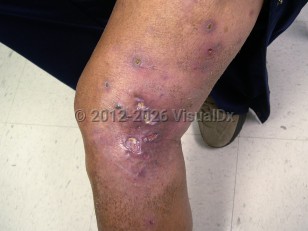
Mycobacterium fortuitum is a rapidly growing nontuberculous mycobacterium. Mycobacterium fortuitum is frequently isolated from the environment, including natural and processed water sources, sewage, and dirt. The most common clinical syndromes that this organism is associated with are skin and soft tissue infection, skeletal infection (bone, joint, and tendon), and catheter-related infections. Surgical site infections are particularly associated with cardiothoracic surgery and have been linked to contamination of the wound with colonized tap water.
Less frequently, infection with this pathogen may cause chronic nodular lung disease or lymphadenitis, especially in the subset of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and chronic vomiting.
Infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a risk factor for M fortuitum infection, although Mycobacterium avium complex and Mycobacterium kansasii are more frequent pathogens in that patient population. Patients with HIV or other severe immunodeficiency are at risk for disseminated infection.
Immunocompetent patients may present with skin infection due to M fortuitum. Most patients will report antecedent trauma. The clinical appearance of the wound is nonspecific.
Mortality due to M fortuitum infection is rare, seen only in patients with disseminated disease or extensive pulmonary disease. Prognosis at most sites is good with debridement and antibiotics. The exception is the lungs, where chronic suppression of the infection and prevention of progression represent the goals of care.
Mycobacterium fortuitum infection
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Codes
ICD10CM:
A31.8 – Other mycobacterial infections
SNOMEDCT:
6040009 – Infection due to Mycobacterium fortuitum
A31.8 – Other mycobacterial infections
SNOMEDCT:
6040009 – Infection due to Mycobacterium fortuitum
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:10/14/2019
Last Updated:10/14/2019
Last Updated:10/14/2019
Mycobacterium fortuitum infection