Avascular necrosis
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis
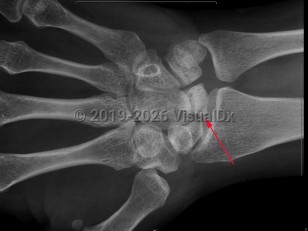
Avascular necrosis (osteonecrosis) is characterized by tissue death due to reduction or loss of blood supply to a bone. Causes include joint or bone trauma, fatty deposits in blood vessels, corticosteroid use, alcohol abuse, and some diseases. Other risk factors are chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and organ transplantation. May occur at any age, but most commonly occurs in adults aged 30-60. Patients are typically asymptomatic early on, but most experience joint pain increasing in severity as the disease develops. The femoral head site is most commonly affected, but the humeral head site, femoral condyles, and small bones are also sites of common occurrence. Typically, clinical presentation consists of sudden onset of pain in the joint.
The goal of treatment is to prevent further joint and bone damage. To help determine the most appropriate treatment (surgical or nonsurgical), the following factors must be taken into account: patient age, stage of disease, affected location, and underlying cause of osteonecrosis.
Related topics: avascular necrosis of knee, avascular necrosis of scaphoid, Köhler disease, osteonecrosis of the femoral heads, osteonecrosis of the humeral heads, progressive avascular necrosis of lunate
The goal of treatment is to prevent further joint and bone damage. To help determine the most appropriate treatment (surgical or nonsurgical), the following factors must be taken into account: patient age, stage of disease, affected location, and underlying cause of osteonecrosis.
Related topics: avascular necrosis of knee, avascular necrosis of scaphoid, Köhler disease, osteonecrosis of the femoral heads, osteonecrosis of the humeral heads, progressive avascular necrosis of lunate
Codes
ICD10CM:
M87.00 – Idiopathic aseptic necrosis of unspecified bone
SNOMEDCT:
86217007 – Avascular necrosis
M87.00 – Idiopathic aseptic necrosis of unspecified bone
SNOMEDCT:
86217007 – Avascular necrosis
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:07/07/2025
Avascular necrosis