Genital herpes simplex virus in Child
See also in: Cellulitis DDx,AnogenitalAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted viral infection caused by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2). The most common pediatric patient is a sexually active adolescent. Infection begins within 10 days after direct contact with active lesions on another infected individual; however, asymptomatic viral shedding is another well-established source of infection.
Sexual abuse must be considered in all young children with genital HSV. Abuse affects children of all ages and backgrounds and, if suspected, needs appropriate referral. Other sources of infection in young children are autoinoculation from herpetic disease of the fingers (herpetic whitlow), innocent inoculation from a caregiver with herpetic whitlow, and close nonsexual physical contact.
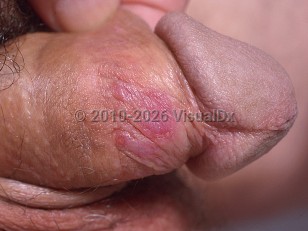
Mucocutaneous HSV infection is characterized by initial outbreaks (primary infection), periods of latency (regional sensory ganglia), and recurrent flares localized to the area of the initial outbreak (recurrent infection).
The initial eruption usually develops within 5-7 days of inoculation and consists of painful vesicles, pustules, and/or erosions on an erythematous base that are scattered over the affected anatomic site. A prodrome of fever, malaise, and lymphadenopathy may precede or accompany the primary mucocutaneous eruption. Recurrent eruptions are usually less severe (fewer lesions, more localized, and less painful), resolve within 1 week, and lack a prodromal phase.
Sexual abuse must be considered in all young children with genital HSV. Abuse affects children of all ages and backgrounds and, if suspected, needs appropriate referral. Other sources of infection in young children are autoinoculation from herpetic disease of the fingers (herpetic whitlow), innocent inoculation from a caregiver with herpetic whitlow, and close nonsexual physical contact.
Mucocutaneous HSV infection is characterized by initial outbreaks (primary infection), periods of latency (regional sensory ganglia), and recurrent flares localized to the area of the initial outbreak (recurrent infection).
The initial eruption usually develops within 5-7 days of inoculation and consists of painful vesicles, pustules, and/or erosions on an erythematous base that are scattered over the affected anatomic site. A prodrome of fever, malaise, and lymphadenopathy may precede or accompany the primary mucocutaneous eruption. Recurrent eruptions are usually less severe (fewer lesions, more localized, and less painful), resolve within 1 week, and lack a prodromal phase.
Codes
ICD10CM:
A60.9 – Anogenital herpesviral infection, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
33839006 – Genital herpes simplex
A60.9 – Anogenital herpesviral infection, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
33839006 – Genital herpes simplex
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:12/14/2016
Last Updated:03/19/2023
Last Updated:03/19/2023
 Patient Information for Genital herpes simplex virus in Child
Patient Information for Genital herpes simplex virus in Child
Premium Feature
VisualDx Patient Handouts
Available in the Elite package
- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient
Upgrade Today

Genital herpes simplex virus in Child
See also in: Cellulitis DDx,Anogenital