Sjögren syndrome in Child
See also in: External and Internal Eye,Oral Mucosal LesionAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

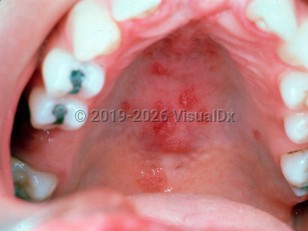
SS most commonly occurs in middle-aged adult women, and there is a similar predominance in pediatric SS patients, who typically present in late childhood / early preteen years with recurrent parotitis. Compared to adults, children with SS are less likely to experience keratoconjunctivitis sicca and xerostomia.
The American-European Consensus Group's (AECG) criteria for primary SS in adults have not been validated in children. AECG criteria include eye symptoms, oral symptoms, findings of keratoconjunctivitis sicca on Schirmer or Rose-Bengal testing, lymphocytic infiltrate of minor salivary glands on biopsy, positive antibodies to SSA or SSB, and salivary gland dysfunction. The addition of recurrent parotitis increases the criteria's sensitivity in children with SS. Given the decreased incidence of xerostomia in children with SS, minor salivary gland biopsy may not have a high yield.
Codes
M35.00 – Sicca syndrome, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
83901003 – Sjögren syndrome
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:05/17/2017