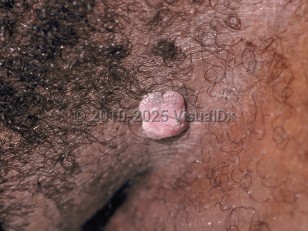
Genital wart in Child
See also in: AnogenitalAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Condyloma acuminata are warts that occur secondary to infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), a double-stranded DNA that belongs to the family of Papillomaviridae. The incubation period from exposure to lesion development can last from months to years.
In children, HPV infections can present as common skin warts, anogenital warts, oral and laryngeal papillomas, and subclinical infections. HPV types 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, and 10 cause skin warts in children, with incidence peaking at ages 12-16 years. HPV types 6 and 11 account for most genital and oral warts, while types 16 and 18 cause both genital warts and genital malignancies. HPV infection causes oropharyngeal and anal cancers in patients of any sex: cervical, vaginal, and vulvar cancer in women and penile cancer in men.
Note: Childhood sexual abuse is a problem of epidemic proportions affecting children of all ages and of all economic and cultural backgrounds. A critical consideration for assessing condyloma acuminata in children is the determination of whether inoculation occurred as a result of sexual abuse. However, anogenital warts from HPV can also occur secondary to perinatal exposure, heteroinoculation (eg, from caregiver a changing diapers), autoinoculation (eg, from a wart on the hand of child), and indirect fomite transfer (eg, from shared towels). Large case series have found that about 3%-10% of anogenital warts in children are due to child sexual abuse.
Related topic: oral mucosal wart
In children, HPV infections can present as common skin warts, anogenital warts, oral and laryngeal papillomas, and subclinical infections. HPV types 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, and 10 cause skin warts in children, with incidence peaking at ages 12-16 years. HPV types 6 and 11 account for most genital and oral warts, while types 16 and 18 cause both genital warts and genital malignancies. HPV infection causes oropharyngeal and anal cancers in patients of any sex: cervical, vaginal, and vulvar cancer in women and penile cancer in men.
Note: Childhood sexual abuse is a problem of epidemic proportions affecting children of all ages and of all economic and cultural backgrounds. A critical consideration for assessing condyloma acuminata in children is the determination of whether inoculation occurred as a result of sexual abuse. However, anogenital warts from HPV can also occur secondary to perinatal exposure, heteroinoculation (eg, from caregiver a changing diapers), autoinoculation (eg, from a wart on the hand of child), and indirect fomite transfer (eg, from shared towels). Large case series have found that about 3%-10% of anogenital warts in children are due to child sexual abuse.
Related topic: oral mucosal wart
Codes
ICD10CM:
A63.0 – Anogenital (venereal) warts
SNOMEDCT:
240542006 – Condyloma acuminatum
A63.0 – Anogenital (venereal) warts
SNOMEDCT:
240542006 – Condyloma acuminatum
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:09/23/2021
Last Updated:09/23/2021
Last Updated:09/23/2021
 Patient Information for Genital wart in Child
Patient Information for Genital wart in Child
Premium Feature
VisualDx Patient Handouts
Available in the Elite package
- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient
Upgrade Today

Genital wart in Child
See also in: Anogenital