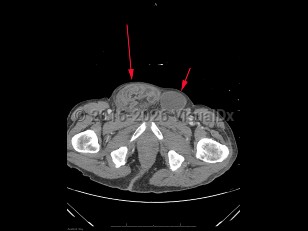
Inguinal hernia in Child
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

An inguinal hernia is a protrusion of an intraabdominal organ, often the small bowel, through an opening in the inguinal area of the abdominal wall. Inguinal hernias are very common, occurring in approximately 5% of the general population. Risk factors include a personal / family history of hernias, history of prior hernia or hernia repair, advanced age, male sex, smoking, prior abdominal wall injury, chronic constipation, and chronic cough. Inguinal hernias can be congenital or acquired. They are caused by a weakening or failed closure of fibromuscular groin tissue.
Symptoms from inguinal hernias can vary considerably. The hernia can be seen as an asymptomatic bulge, can cause intermittent discomfort, or be an acute emergency with severe abdominal pain, bowel obstruction, and sepsis if strangulation or bowel obstruction develops. Symptoms typically worsen with increased intraabdominal pressure (eg, prolonged standing, weight lifting).
Inguinal hernias can be classified as either direct or indirect, determined by their location. An indirect inguinal hernia's defect is at the internal inguinal ring. A direct inguinal hernia's defect is medial to the inferior epigastric vessels within Hesselbach's triangle. Indirect inguinal hernias are more common and are often attributed to congenital defects; direct inguinal hernias are often acquired in the setting of connective tissue weaknesses.
Symptoms from inguinal hernias can vary considerably. The hernia can be seen as an asymptomatic bulge, can cause intermittent discomfort, or be an acute emergency with severe abdominal pain, bowel obstruction, and sepsis if strangulation or bowel obstruction develops. Symptoms typically worsen with increased intraabdominal pressure (eg, prolonged standing, weight lifting).
Inguinal hernias can be classified as either direct or indirect, determined by their location. An indirect inguinal hernia's defect is at the internal inguinal ring. A direct inguinal hernia's defect is medial to the inferior epigastric vessels within Hesselbach's triangle. Indirect inguinal hernias are more common and are often attributed to congenital defects; direct inguinal hernias are often acquired in the setting of connective tissue weaknesses.
Codes
ICD10CM:
K40.90 – Unilateral inguinal hernia, without obstruction or gangrene, not specified as recurrent
SNOMEDCT:
396232000 – Inguinal Hernia
K40.90 – Unilateral inguinal hernia, without obstruction or gangrene, not specified as recurrent
SNOMEDCT:
396232000 – Inguinal Hernia
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:01/10/2018
Last Updated:01/10/2018
Last Updated:01/10/2018
Inguinal hernia in Child