In neonates, Candida is a common cause of mucous membrane infections including oral candidiasis, or thrush. Cutaneous candidiasis includes generalized cutaneous candidiasis, candidal intertrigo, erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica, and perineal skin infections. Paronychia and onychomycosis, diaper dermatitis, and chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis are also cutaneous syndromes.
Deep visceral involvement occurs with disseminated or systemic candidiasis. Approximately 5% of low-birth-weight infants are affected.
Mucous membrane infection:
- Thrush, or oral candidiasis, is normally seen in infants younger than 1 year.
- Generalized cutaneous candidiasis is an eruption of lesions covering the trunk, thorax, and extremities; lesions are accentuated in the genitocrural folds and around the anus as well as the axillae, hands, and feet. The skin is erythematous, and lesions are initially discrete and then coalesce into larger plaques. Fissuring of the skin may be present.
- Candidal intertrigo occurs where skin surfaces are closely apposed to each other. The most common sites are the axillary, inframammary, gluteal, and genitocrural regions. Intertrigo results from widespread colonization, especially of macerated folds of moist skin. This usually presents as inflammation of the skin folds and starts as vesicles and pustules. The skin appears erythematous with surrounding vesicles and pustules.
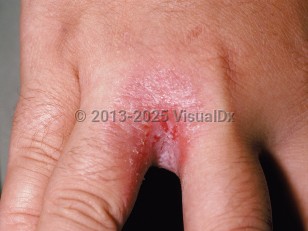
- Erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica is candidal infection of the web spaces of the fingers and the toes. The skin lesions appear red and macerated and may extend onto the digits. Pustules may also be present. The toxic dermatitis initiated by Candida species is usually followed by infection with gram-negative rods, exacerbating the chronicity of the lesion.
- Candidal folliculitis is infection of the hair follicles. Although usually localized, it can become widespread and must be differentiated from folliculitis caused by dermatophytes and tinea versicolor.
- Candidal balanitis presents as vesicles on the penis that cause intense itching and burning. The lesions may also spread to the scrotum, thighs, and gluteal folds. See male genital candidiasis.
- Angular cheilitis can be caused by candidal infection of the angles of the mouth and results in macerated skin with deep creases and crust formation.



 Patient Information for
Patient Information for