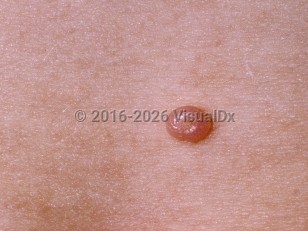
Molluscum contagiosum (pediatric) in Infant/Neonate
See also in: AnogenitalAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

This summary discusses pediatric patients. Molluscum contagiosum in adults is addressed separately.
Molluscum contagiosum is a common viral skin infection of childhood caused by a DNA poxvirus. It is usually transmitted by direct skin-to-skin contact, through fomites, or from autoinoculation. There is an increased incidence in children with underlying atopic dermatitis or other conditions with filaggrin gene mutations (such as ichthyosis vulgaris), swimmers, children who bathe together, those who share towels, and immunosuppressed people.
Infection is infrequent in newborns and infants. The rarity of the condition in those aged younger than one year is thought to reflect transmitted immunity through maternal antibodies.
The exact incubation period is unknown but is estimated to be between 2 and 6 weeks. Alhough it is self-limited, the infection is often chronic and can range from a few months to 4 years, often with transmission to household members during this time.
Molluscum can be found anywhere on the body. Genital involvement does not absolutely imply sexual transmission, as molluscum may be autoinoculated from a nongenital site to the genital area. A thorough history will direct suspicion for sexual abuse in these cases.
Molluscum contagiosum is a common viral skin infection of childhood caused by a DNA poxvirus. It is usually transmitted by direct skin-to-skin contact, through fomites, or from autoinoculation. There is an increased incidence in children with underlying atopic dermatitis or other conditions with filaggrin gene mutations (such as ichthyosis vulgaris), swimmers, children who bathe together, those who share towels, and immunosuppressed people.
Infection is infrequent in newborns and infants. The rarity of the condition in those aged younger than one year is thought to reflect transmitted immunity through maternal antibodies.
The exact incubation period is unknown but is estimated to be between 2 and 6 weeks. Alhough it is self-limited, the infection is often chronic and can range from a few months to 4 years, often with transmission to household members during this time.
Molluscum can be found anywhere on the body. Genital involvement does not absolutely imply sexual transmission, as molluscum may be autoinoculated from a nongenital site to the genital area. A thorough history will direct suspicion for sexual abuse in these cases.
Codes
ICD10CM:
B08.1 – Molluscum contagiosum
SNOMEDCT:
40070004 – Infection caused by Molluscum contagiosum
B08.1 – Molluscum contagiosum
SNOMEDCT:
40070004 – Infection caused by Molluscum contagiosum
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:05/06/2025
 Patient Information for Molluscum contagiosum (pediatric) in Infant/Neonate
Patient Information for Molluscum contagiosum (pediatric) in Infant/Neonate
Premium Feature
VisualDx Patient Handouts
Available in the Elite package
- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient
Upgrade Today

Molluscum contagiosum (pediatric) in Infant/Neonate
See also in: Anogenital