Lichen planus - Anogenital in
See also in: Overview,Nail and Distal DigitAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

LP of the male genitalia typically occurs in uncircumcised adult males, with a reported median age of onset at 51 years. In the vast majority of reported cases, only the genitalia are involved.
However, sometimes the skin is affected more broadly, and LP can also affect hair follicles, nail units, and mucous membranes. See oral LP for oral mucosal presentation, and see lichen planopilaris for scalp presentation.
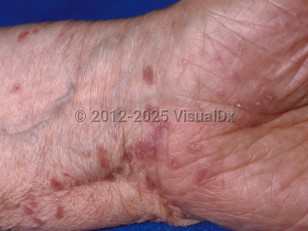
Clinically, LP presents with flat-topped, reddish-to-purple papules. Penile LP most commonly presents on the glans penis and is often annular in configuration. Most cases are asymptomatic. Papules and plaques can rarely erode, resulting in significant pain, scarring, and impairment of sexual function.
Drugs causing LP-like eruptions (lichenoid drug reactions) include antihypertensives (angiotensin-converting enzyme [ACE] inhibitors such as captopril and enalapril; beta blockers such as propranolol and labetalol), thiazide diuretics, antimalarials (quinidine and hydroxychloroquine), penicillamine, NSAIDs, griseofulvin, tetracycline, antiepileptics, and many other drugs.
LP can spontaneously resolve, usually after a year, or follow a remitting or chronic course.
Codes
L43.9 – Lichen planus, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
4776004 – Lichen planus
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:01/28/2025
 Patient Information for Lichen planus - Anogenital in
Patient Information for Lichen planus - Anogenital in - Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient