Desquamative gingivitis - Oral Mucosal Lesion
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

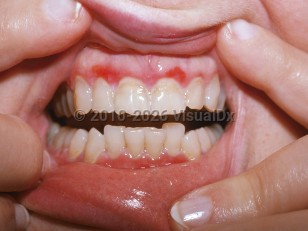
Desquamative gingivitis, also referred to as erosive gingivostomatitis, is a term used to describe a reaction pattern in the oral mucosa characterized by epithelial desquamation, vesiculobullous lesions, erythema, and/or erosions of the gingiva. Desquamative gingivitis is not a specific diagnosis. The differential diagnosis is broad, ranging from irritant dermatitis, foreign body gingivitis, and allergic reactions (including lichenoid contact dermatitis, lichenoid drug reaction, and fixed drug eruption), to autoinflammatory conditions (including lichen planus, erythema multiforme, lupus erythematosus [most commonly discoid lupus erythematosus], and graft-versus-host disease), to autoimmune bullous diseases (including pemphigus vulgaris, mucous membrane pemphigoid, paraneoplastic pemphigus, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, and linear IgA bullous dermatosis). The conditions responsible for most cases are oral lichen planus, mucous membrane pemphigoid, and pemphigus vulgaris.
Patients affected by desquamative gingivitis will frequently experience intense discomfort and may have difficulty eating and drinking. Lesions typically arise along the buccal aspect of the gingiva, most commonly in a diffuse pattern. However, lesions have been reported to occur at any site along the gingiva.
If the desquamative gingivitis is a manifestation of mucous membrane pemphigoid, pemphigus vulgaris, or paraneoplastic pemphigus, the patient may develop extra-oral involvement in other sites, most commonly the nasal or anogenital mucosa, larynx, esophagus, skin, and conjunctiva.
Patients affected by desquamative gingivitis will frequently experience intense discomfort and may have difficulty eating and drinking. Lesions typically arise along the buccal aspect of the gingiva, most commonly in a diffuse pattern. However, lesions have been reported to occur at any site along the gingiva.
If the desquamative gingivitis is a manifestation of mucous membrane pemphigoid, pemphigus vulgaris, or paraneoplastic pemphigus, the patient may develop extra-oral involvement in other sites, most commonly the nasal or anogenital mucosa, larynx, esophagus, skin, and conjunctiva.
Codes
ICD10CM:
K05.11 – Chronic gingivitis, non-plaque induced
SNOMEDCT:
22208002 – Desquamative gingivitis
K05.11 – Chronic gingivitis, non-plaque induced
SNOMEDCT:
22208002 – Desquamative gingivitis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:05/02/2021
Last Updated:05/02/2021
Last Updated:05/02/2021
Desquamative gingivitis - Oral Mucosal Lesion