Optic neuritis - External and Internal Eye
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

In the United States, the prevalence of optic neuritis in a predominately white population is 115 per 100,000. Most cases occur in white women between the ages of 15 and 45.
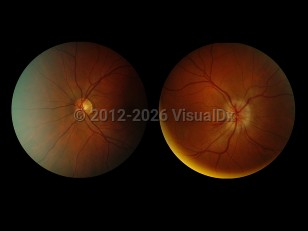
Patients with idiopathic acute optic neuritis typically present with pain and unilateral visual loss over days without systemic or neurological symptoms. Pain is present in more than 90% of cases and often worsens with eye movements. The extent of vision loss can vary and is associated with a loss of color perception. One-third of cases of optic neuritis involve swelling of the optic disc, while most cases have a normal funduscopic examination with retrobulbar optic nerve involvement. As optic neuritis is usually unilateral, an afferent pupillary defect is usually present.
Pediatric Patient Considerations:
While children may experience bilateral optic neuritis more commonly, involvement of both eyes should prompt a search for other causes.
Codes
H46.9 – Unspecified optic neuritis
SNOMEDCT:
66760008 – Optic neuritis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required