Uncombable hair syndrome - Hair and Scalp
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

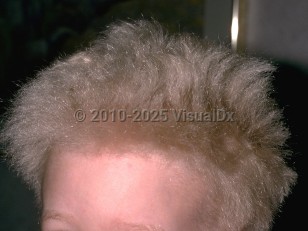
Uncombable hair syndrome is a rare structural anomaly of the hair that usually presents in early childhood. The condition may present any time from infancy until age 12 but typically presents between the ages of 3 months and 3 years, with spontaneous improvement often occurring in later childhood. The hair is usually silver-blond or straw-colored (spun glass hair) and cannot lie flat. It grows at a normal rate or more slowly and is of normal quantity and length. Hair is not fragile or brittle, and cannot be easily extracted from the scalp. Males and females are equally affected. The descriptive term for this condition is pili trianguli et canaliculi. It is also known as "mop hair."
On microscopic examination, the hair shaft has characteristic irregular twists along its axis at regular intervals. These irregular twists are what makes the hair difficult to comb and prevents the hair from grouping with adjacent hair in an organized fashion, contributing to the unruly appearance. It also has triangular to reniform shape on cross section, with longitudinal grooves along the entire length of the hair shaft. The cause of the malformed hair has been attributed to an altered inner root sheath that then gives rise to an abnormal hair shaft.
Familial cases occur and show autosomal dominant inheritance with incomplete penetrance. Recessive forms exist, with variable penetrance, and sporadic cases have also been reported. There are also acquired and partial variants. The acquired form presents later in life and is more common among individuals with dark and/or curly hair. The partial variant is confined to a well-demarcated area of hair on the scalp with the characteristic features of uncombable hair syndrome.
Associated features of ectodermal dysplasia have been reported in some cases.
On microscopic examination, the hair shaft has characteristic irregular twists along its axis at regular intervals. These irregular twists are what makes the hair difficult to comb and prevents the hair from grouping with adjacent hair in an organized fashion, contributing to the unruly appearance. It also has triangular to reniform shape on cross section, with longitudinal grooves along the entire length of the hair shaft. The cause of the malformed hair has been attributed to an altered inner root sheath that then gives rise to an abnormal hair shaft.
Familial cases occur and show autosomal dominant inheritance with incomplete penetrance. Recessive forms exist, with variable penetrance, and sporadic cases have also been reported. There are also acquired and partial variants. The acquired form presents later in life and is more common among individuals with dark and/or curly hair. The partial variant is confined to a well-demarcated area of hair on the scalp with the characteristic features of uncombable hair syndrome.
Associated features of ectodermal dysplasia have been reported in some cases.
Codes
ICD10CM:
L67.8 – Other hair color and hair shaft abnormalities
SNOMEDCT:
254230001 – Uncombable hair syndrome
L67.8 – Other hair color and hair shaft abnormalities
SNOMEDCT:
254230001 – Uncombable hair syndrome
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:01/25/2022
Uncombable hair syndrome - Hair and Scalp