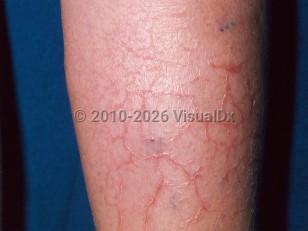
Eczema craquelé
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Xerosis is the predisposing factor to the development of eczema craquelé. The pathogenesis involves a decrease in the amount of lipids in the stratum corneum and a deficiency in the water-binding capacity of this layer. The condition is seen mostly in older adults; however, it can be associated with a number of environmental factors and/or disease states, such as low humidity, frequent bathing, harsh soaps, congenital and acquired ichthyoses, atopic dermatitis, hypothyroidism, Down syndrome, renal failure, malnutrition and malabsorptive states, HIV infection, lymphoma, liver disease, Sjögren syndrome, carcinomatosis, graft-versus-host disease, zinc deficiency, and certain drugs (in particular retinoids, diuretics, and protein kinase inhibitors).
Codes
L85.3 – Xerosis cutis
SNOMEDCT:
201077008 – Asteatotic eczema
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:04/17/2025
 Patient Information for Eczema craquelé
Patient Information for Eczema craquelé - Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient