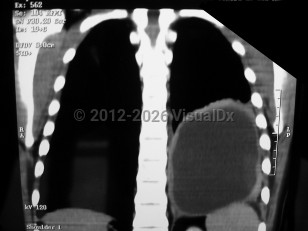
CE is the most common cause of hydatid disease; it involves a definitive host (dog) and an intermediate herbivorous animal (sheep, cattle). Humans may accidentally become infected through ingestion of food or water contaminated with eggs or from contact with the fur of an infected dog. CE leads to slowly growing hepatic (70%) and/or pulmonary (20%) cystic lesions that can be asymptomatic for a variable time period (5-20 years). Cysts may be complicated by bacterial superinfection, cyst rupture, and anaphylactic shock.
AE involves wolves and dogs as definitive hosts and mice as intermediate hosts, with humans becoming infected through fecal-oral contact. AE is also a slowly advancing infection, although after a variable incubation period of 5-15 years, it differentiates itself from CE by producing multiple small vesicles infecting the liver initially, with subsequent metastatic spread to other organs (lungs, brain, bone, etc) in 20%-30% of cases. AE may be fatal if not treated.
CE has a nearly worldwide geographical distribution, although most cases reported in the United States are imported from European Mediterranean countries, the Russian Federation, China, Africa, Australia, and South America. AE is restricted to the northern hemisphere, with cases reported from Alaska and Canada in North America; Switzerland, Germany, and France in Europe; the tundra region of the Russian Federation; and the northern parts of China and Japan.
The initial phase of both CE and AE infection is asymptomatic. Cysts may grow slowly over months or even years. The infection may become symptomatic if the cysts either rupture or exert mass effect.
- For liver involvement, abdominal pain and jaundice may occur with large cysts distending the liver capsule or compressing the biliary tree, while signs and symptoms of cholangitis or even anaphylaxis may present if cysts rupture.
- For lung involvement, dyspnea can occur with large cyst(s) compressing lung parenchyma, while fever and cough productive of "salty" sputum may be the presenting signs of pulmonary cyst rupture.
- The clinical presentation of the less common locations (ie, cardiac, renal, muscular, or subcutaneous) is usually caused by mass effect.
Infection can be life-threatening in special situations (anaphylaxis) and in advanced cases, but by and large echinococcosis is a chronic condition.