Iododerma
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

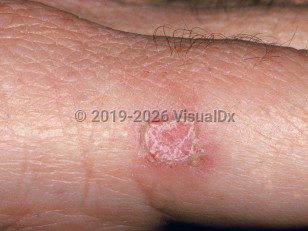
Iododerma most commonly affects sebaceous areas (eg, face), but some cases involve the trunk, extremities, and mucous membranes. It has been associated with swelling of the major salivary glands. The cutaneous lesions of iododerma may include vesicular, pustular, acneiform, hemorrhagic, urticarial, fungating, suppurative, and ulcerative.
Decreased renal function in those receiving iodinated contrast media may increase risk of reaction, though iododerma has been reported in patients with normal renal function. Vegetating iododerma has been associated with polyarteritis nodosa and paraproteinemias such as multiple myeloma.
Though the pathogenesis of iododerma is not completely understood, it is thought to be related to a hypersensitivity reaction to iodine.
Codes
L27.8 – Dermatitis due to other substances taken internally
SNOMEDCT:
89414003 – Iododerma
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required