Pediculosis pubis
See also in: AnogenitalAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

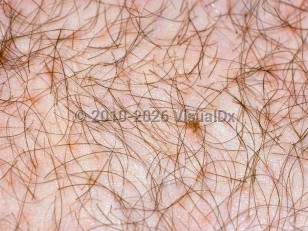
Pediculosis pubis (pubic lice or crabs) is a highly contagious, sexually transmitted parasitic infestation with the pubic or crab louse, Phthirus pubis. Disease is most often spread from person to person by close physical contact, but it may occasionally be spread via fomites such as clothing or linens. Household pets do not play a role in transmission.
Epidemiology is difficult to elucidate as the infection is likely under-recognized and can be treated without presentation to a health care provider. However, this condition is more common in sexually active individuals. Lice live on terminal hair, typically in the pubic and perianal regions, although infestations may also be noted in the eyelashes (pediculosis palpebrarum), eyebrows, and other facial hair, as well as chest and axillary hair. Scalp infestation may also be seen in tightly curled hair. The lice are not adapted for crawling.
The incubation time is less than one week from contact, although it has been found to be longer in some cases. The eggs (nits) are cemented to hair shafts with chitin and are difficult to remove. Lice hatch in approximately 6-10 days. The lifespan of the louse is less than 1 month. The lice are not able to survive without feeding within 24 hours.
Although the bites of the lice are thought to be painless, the majority of those infected will present with extreme pruritus; one study suggests up to 86% will complain of pruritus. This is thought to be secondary to a reaction to the saliva and/or the anticoagulant injected into the skin by the louse during feeding.
Epidemiology is difficult to elucidate as the infection is likely under-recognized and can be treated without presentation to a health care provider. However, this condition is more common in sexually active individuals. Lice live on terminal hair, typically in the pubic and perianal regions, although infestations may also be noted in the eyelashes (pediculosis palpebrarum), eyebrows, and other facial hair, as well as chest and axillary hair. Scalp infestation may also be seen in tightly curled hair. The lice are not adapted for crawling.
The incubation time is less than one week from contact, although it has been found to be longer in some cases. The eggs (nits) are cemented to hair shafts with chitin and are difficult to remove. Lice hatch in approximately 6-10 days. The lifespan of the louse is less than 1 month. The lice are not able to survive without feeding within 24 hours.
Although the bites of the lice are thought to be painless, the majority of those infected will present with extreme pruritus; one study suggests up to 86% will complain of pruritus. This is thought to be secondary to a reaction to the saliva and/or the anticoagulant injected into the skin by the louse during feeding.
Codes
ICD10CM:
B85.3 – Phthiriasis
SNOMEDCT:
71011005 – Pediculosis pubis
B85.3 – Phthiriasis
SNOMEDCT:
71011005 – Pediculosis pubis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:12/20/2017
Last Updated:12/20/2017
Last Updated:12/20/2017
 Patient Information for Pediculosis pubis
Patient Information for Pediculosis pubis
Premium Feature
VisualDx Patient Handouts
Available in the Elite package
- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient
Upgrade Today

Pediculosis pubis
See also in: Anogenital