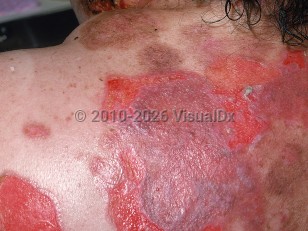
Pemphigus vulgaris in Child
See also in: Anogenital,Oral Mucosal LesionAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

PV typically affects adults, with a mean age of onset in the fifth and sixth decades of life. Variants of the ST18 gene have been found to confer increased risk of PV in some populations.
Childhood PV, which refers to disease in children younger than 12 years, and juvenile PV, which refers to disease in adolescents aged 13-18 years, are rare, comprising less than 5% of all cases. The mucocutaneous type is more frequently observed in children and adolescents.
PV is characterized by painful erosions on the oral mucosa and flaccid bullae and erosions on the skin. Severe cases of PV can be life-threatening, and complications can be related to immunosuppression from drugs used to treat severe PV, secondary infections, loss of the skin barrier, and poor oral intake.
Codes
L10.0 – Pemphigus vulgaris
SNOMEDCT:
49420001 – Pemphigus vulgaris
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:01/10/2022
 Patient Information for Pemphigus vulgaris in Child
Patient Information for Pemphigus vulgaris in Child- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient