Torus palatinus - Oral Mucosal Lesion
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

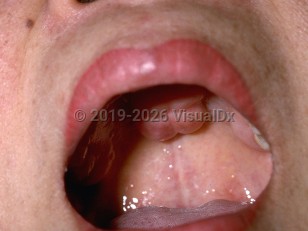
Torus Palatinus is an exostosis, a benign localized bony protuberance on the midline of the palate. Tori on the lingual mandible are referred to as torus mandibularis and are discussed separately. Tori (palatinus and mandibularis) are likely caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. They tend to occur more often in the Asian and Inuit population with a slight female predilection. They are most commonly noticed during the early adult years. Patients are often unaware of the presence of tori since they usually have been present for a long time and grow very slowly. Some cases exhibit a "growth spurt" and patients become aware of a fairly rapidly enlarging mass.
Genetic and environmental factors (such as chronic irritation) likely play a role in the development of these lesions. Some tori may also regress or become smaller over time. Tori are usually painless unless the areas are traumatized.
Genetic and environmental factors (such as chronic irritation) likely play a role in the development of these lesions. Some tori may also regress or become smaller over time. Tori are usually painless unless the areas are traumatized.
Codes
ICD10CM:
M27.0 – Developmental disorders of jaws
SNOMEDCT:
46752004 – Palatal torus
M27.0 – Developmental disorders of jaws
SNOMEDCT:
46752004 – Palatal torus
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:01/25/2022
Torus palatinus - Oral Mucosal Lesion