Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
See also in: External and Internal Eye,Oral Mucosal LesionAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

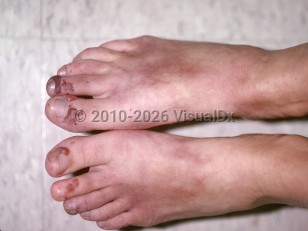
The disease typically presents with upper airway disease and nonspecific complaints such as malaise, arthralgias, fever, and weight loss. Respiratory tract symptoms include sinusitis, otitis media, rhinorrhea, cough, sputum production, chest pain, dyspnea, and hemoptysis. Ocular involvement occurs in 30%-50% of patients with GPA and can occur without systemic manifestations. Oral lesions can be seen with any of the clinical presentations of GPA and consist of ulcerations and/or "strawberry" gingivitis.
The disease presents variably on a continuum from limited involvement (which may remain limited for variable periods of time) to a more generalized form with involvement of the upper and lower respiratory tract, kidney, skin, and other organs. Untreated, the generalized form is fatal in less than 2 years; however, with the advent of cytotoxic therapy, long-term remissions are possible in more than 90% of patients.
Complications of GPA include pericarditis, coronary arteritis, myocardial infarction, pancarditis, granulomatous valvulitis, mononeuritis multiplex, and polyneuritis. Laryngotracheal stenosis with stridor can be a complication of GPA and initially may be misdiagnosed as asthma.
Codes
M31.30 – Wegener's granulomatosis without renal involvement
M31.31 – Wegener's granulomatosis with renal involvement
SNOMEDCT:
195353004 – Wegener's granulomatosis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:05/17/2020