Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

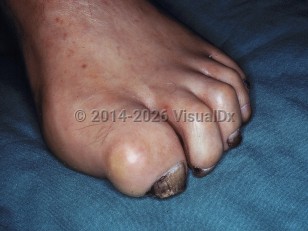
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) is a genetically and clinically heterogeneous polyneuropathy characterized by progressive motor and sensory deficits. It is one of the most common inherited causes of neuropathy. Symptoms of weakness in the limbs and sometimes the hands are often first noted in late childhood or early adulthood. It may be accompanied with mild to moderate sensory loss and sometimes neuropathic pain. There is usually some atrophy of small muscles in the hands and feet. Deep tendon reflexes are often depressed, and it is common for pes cavus (a fixed plantar flexion, ie, the arch of the foot does not flatten when bearing weight) and hammer toes to develop. Several dominant forms of CMT are related to mutations in a tRNA synthetase and activation of a integrated stress response.
CMT can be subdivided into two large groups on the basis of electrophysiologic criteria: CMT1 is the demyelinating form and CMT2 the axonal form. Patients with primarily distal motor neuropathy are sometimes considered to comprise a third type. Nerve conduction velocity is reduced and electromyography can also be diagnostically helpful. It may be helpful to look for characteristic changes such as loss of myelinated fibers and the presence of focal myelin sheath folding in sural nerve biopsies.
Early-onset glaucoma, optic atrophy, and sensorineural hearing loss are found in some families. Dementia and intellectual deficits are not generally a part of CMT.
CMT can be subdivided into two large groups on the basis of electrophysiologic criteria: CMT1 is the demyelinating form and CMT2 the axonal form. Patients with primarily distal motor neuropathy are sometimes considered to comprise a third type. Nerve conduction velocity is reduced and electromyography can also be diagnostically helpful. It may be helpful to look for characteristic changes such as loss of myelinated fibers and the presence of focal myelin sheath folding in sural nerve biopsies.
Early-onset glaucoma, optic atrophy, and sensorineural hearing loss are found in some families. Dementia and intellectual deficits are not generally a part of CMT.
Codes
ICD10CM:
G60.0 – Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy
SNOMEDCT:
398100001 – Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy
G60.0 – Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy
SNOMEDCT:
398100001 – Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:09/12/2021
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease