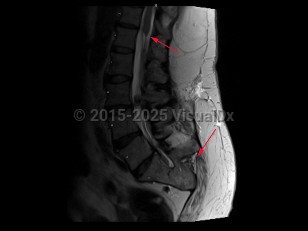
Caudal regression syndrome in Infant/Neonate
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Congenital abnormality characterized by malformation or absence of the sacrum, usually with associated spinal dysraphism and tethered cord. Presentation can range from mild to life-threatening. It may be an isolated defect or can be found as part of associated syndromes, such as the VACTERL association (vertebral defects, anal atresia, cardiac defects, tracheo-esophageal abnormalities, renal and radial abnormalities, and limb abnormalities).
Other characteristics include narrow hips, hypoplastic gluteal muscles, short intergluteal cleft, sacral dimple, lower limb flexion contractures, clubfeet, and leg atrophy. Neurological abnormalities such as poorly controlled urinary and bowel function are often observed. Most commonly seen in infants born to birthing parents with diabetes. Treatment is symptomatic.
Other characteristics include narrow hips, hypoplastic gluteal muscles, short intergluteal cleft, sacral dimple, lower limb flexion contractures, clubfeet, and leg atrophy. Neurological abnormalities such as poorly controlled urinary and bowel function are often observed. Most commonly seen in infants born to birthing parents with diabetes. Treatment is symptomatic.
Codes
ICD10CM:
Q87.89 – Other specified congenital malformation syndromes, not elsewhere classified
SNOMEDCT:
8301004 – Caudal dysplasia sequence
Q87.89 – Other specified congenital malformation syndromes, not elsewhere classified
SNOMEDCT:
8301004 – Caudal dysplasia sequence
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:05/11/2025
Caudal regression syndrome in Infant/Neonate