Developmental dysplasia of the hip in Child
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis
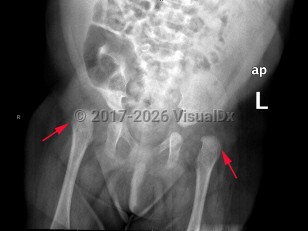
A spectrum of developmental abnormalities of hip joint dislocation or subluxation of the acetabulum and proximal femur (head), typically diagnosed in infants and children. Most often unilateral, but may be bilateral (20%). Common signs and symptoms include hip instability, pain, limited range of motion, abnormal gait, and limping. It may be associated with breech birth, family history, or social practice of swaddling. Some neuromuscular disorders may be associated with hip dysplasia. Early intervention decreases lasting and progressive damage, limiting functional disability and preventing early-onset osteoarthritis. Many cases of infant hip instability will gradually stabilize.
Treatments for more severe dysplasia include harnesses and splints (braces) for infants prior to walking, abduction brace orthosis, surgical reduction, spica cast, and hip reconstruction, depending on the age of the patient and progression of the dysplasia.
Treatments for more severe dysplasia include harnesses and splints (braces) for infants prior to walking, abduction brace orthosis, surgical reduction, spica cast, and hip reconstruction, depending on the age of the patient and progression of the dysplasia.
Codes
ICD10CM:
Q65.00 – Congenital dislocation of unspecified hip, unilateral
SNOMEDCT:
48334007 – Congenital dislocation of hip
Q65.00 – Congenital dislocation of unspecified hip, unilateral
SNOMEDCT:
48334007 – Congenital dislocation of hip
Best Tests
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:02/09/2016
Developmental dysplasia of the hip in Child