CS tear gas intoxication - Chem-Bio-Rad Suspicion
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

CS, CN (also known as mace), OC (also known as pepper spray), and CR are commonly known as tear gas or lacrimators and are riot control agents that serve to temporarily incapacitate those exposed. They are relatively safe due to a high LCt50* and low effective Ct50, and the effects are short lived once the agent is removed.
Riot control agents are not considered chemical warfare agents as defined by the Geneva Convention of 1925, and they are utilized by police forces worldwide.
Tear gas is disseminated as a smoke or large particle mist via spray can, tank, grenade, or larger bombs.
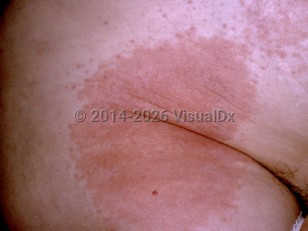
CS, CN, and CR primarily affect the eyes, causing temporary blindness due to lacrimation and blepharospasm. They also produce conjunctival redness; mouth, nose, and throat irritation; cough; chest tightness; and sneezing. In raw or abraded skin, lacrimators can cause burning and erythema. Under the conditions of high temperature, high humidity, and high concentration, they can cause second-degree burns with erythema and vesication. The effects of these agents are felt on contact and, once the agent is removed, dissipate within 15-30 minutes. The effects of OC are usually limited to runny nose and watery eyes.
*LCt50 (L = lethal, C = concentration of vapor [mg/m3], t = exposure time [minutes]) is the concentration of a chemical agent exposure by inhalation that causes death in 50% of unprotected people.
Riot control agents are not considered chemical warfare agents as defined by the Geneva Convention of 1925, and they are utilized by police forces worldwide.
Tear gas is disseminated as a smoke or large particle mist via spray can, tank, grenade, or larger bombs.
CS, CN, and CR primarily affect the eyes, causing temporary blindness due to lacrimation and blepharospasm. They also produce conjunctival redness; mouth, nose, and throat irritation; cough; chest tightness; and sneezing. In raw or abraded skin, lacrimators can cause burning and erythema. Under the conditions of high temperature, high humidity, and high concentration, they can cause second-degree burns with erythema and vesication. The effects of these agents are felt on contact and, once the agent is removed, dissipate within 15-30 minutes. The effects of OC are usually limited to runny nose and watery eyes.
*LCt50 (L = lethal, C = concentration of vapor [mg/m3], t = exposure time [minutes]) is the concentration of a chemical agent exposure by inhalation that causes death in 50% of unprotected people.
Codes
ICD10CM:
T59.3X4A – Toxic effect of lacrimogenic gas, undetermined, initial encounter
SNOMEDCT:
84419005 – Tear gas toxic effect
T59.3X4A – Toxic effect of lacrimogenic gas, undetermined, initial encounter
SNOMEDCT:
84419005 – Tear gas toxic effect
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:06/04/2013
CS tear gas intoxication - Chem-Bio-Rad Suspicion