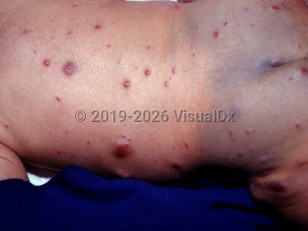
Diffuse neonatal hemangiomatosis
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Diffuse neonatal hemangiomatosis is characterized by multiple hemangiomatous lesions present at birth or that develop rapidly within the first few days of life. In diffuse neonatal hemangiomatosis, multiple cutaneous and visceral hemangiomas can lead to life-threatening complications. Potential involved organs include the gastrointestinal (GI) tract (leading to GI bleeding), larynx, lungs, central nervous system, spleen, and liver. Arteriovenous (AV) shunts and hepatic involvement can lead to high-output cardiac failure and death. Mortality is estimated to be over 50%. Cerebral hemorrhage is another cause of death. Infants presenting with multiple disseminated hemangiomas need to be evaluated and managed aggressively.
Codes
ICD10CM:
D18.01 – Hemangioma of skin and subcutaneous tissue
SNOMEDCT:
254782003 – Multiple progressive hemangiomata
D18.01 – Hemangioma of skin and subcutaneous tissue
SNOMEDCT:
254782003 – Multiple progressive hemangiomata
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:02/01/2022
Diffuse neonatal hemangiomatosis