Subungual wart in Adult
See also in: Nail and Distal DigitAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Warts are an infection of the epidermis with human papillomavirus (HPV). Warts that involve the periungual skin or subungual area are typically associated with HPV subtypes 1, 2, 4, 27, and 57. Butcher's warts may also affect the nail apparatus and are due to HPV 2 and 7. Warts are the most common nail tumor and affect fingernails more frequently than toenails. Warts are spread by human contact or indirectly via fomites on surfaces. Infection is more likely to occur when the skin is macerated or traumatized.
In adults, warts are especially common among transplant patients and in individuals who are immunosuppressed due to HIV infection, malignancy, or medications. They are also common in adults who do wet work, as well as in nail biters and nail pickers. There is a subset of ungual warts due to HPV 16 and 18 that are at higher risk of transforming into squamous cell carcinoma.
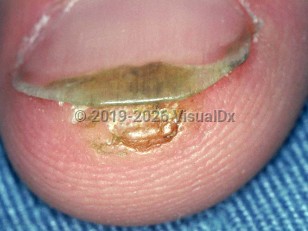
Ungual warts are characterized as periungual, those that occur around the nail unit, or subungual, those that occur beneath the nail unit. A given patient may have both periungual warts and subungual warts. Subungual warts typically present as nodular lesions that uplift the nail plate or as linear growths that penetrate underneath the nail plate, producing a longitudinal band of onycholysis and splinter hemorrhages. Subungual warts may be painful, and the pain may be so severe that it mimics the pain of a glomus tumor. Subungual warts rarely resolve spontaneously.
Complications of ungual warts include bone erosions, spreading to the lips in nail biters, and, rarely, progression to squamous cell carcinoma. Progression to squamous cell carcinoma is more common in immunosuppressed individuals.
In adults, warts are especially common among transplant patients and in individuals who are immunosuppressed due to HIV infection, malignancy, or medications. They are also common in adults who do wet work, as well as in nail biters and nail pickers. There is a subset of ungual warts due to HPV 16 and 18 that are at higher risk of transforming into squamous cell carcinoma.
Ungual warts are characterized as periungual, those that occur around the nail unit, or subungual, those that occur beneath the nail unit. A given patient may have both periungual warts and subungual warts. Subungual warts typically present as nodular lesions that uplift the nail plate or as linear growths that penetrate underneath the nail plate, producing a longitudinal band of onycholysis and splinter hemorrhages. Subungual warts may be painful, and the pain may be so severe that it mimics the pain of a glomus tumor. Subungual warts rarely resolve spontaneously.
Complications of ungual warts include bone erosions, spreading to the lips in nail biters, and, rarely, progression to squamous cell carcinoma. Progression to squamous cell carcinoma is more common in immunosuppressed individuals.
Codes
ICD10CM:
B07.8 – Other viral warts
SNOMEDCT:
240535006 – Subungual wart
B07.8 – Other viral warts
SNOMEDCT:
240535006 – Subungual wart
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:05/13/2018
Last Updated:07/08/2020
Last Updated:07/08/2020
Subungual wart in Adult
See also in: Nail and Distal Digit