Nodular episcleritis - External and Internal Eye
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

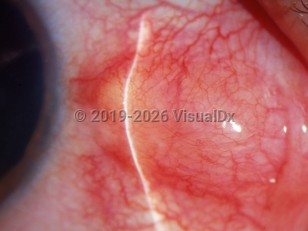
Nodular episcleritis is a frequently recurring inflammatory condition of the episcleral tissue. Onset is usually acute and can be unilateral or bilateral. Nodular episcleritis, as opposed to diffuse episcleritis, implies a discrete area of elevated, inflamed episcleral tissue. Symptoms may be asymptomatic or include irritation, photophobia, tearing, and mild tenderness to palpation.
Most cases are idiopathic; however, 26%-36% of patients have an associated underlying systemic condition. Unlike the diffuse form of the disease, most episodes of nodular episcleritis are of a more indolent and longer duration, and may require topical and/or systemic treatment.
The incidence is higher in women and is more common in the fourth to fifth decades. Recurrences may be of either the diffuse type or the nodular type of episcleritis.
Most cases are idiopathic; however, 26%-36% of patients have an associated underlying systemic condition. Unlike the diffuse form of the disease, most episodes of nodular episcleritis are of a more indolent and longer duration, and may require topical and/or systemic treatment.
The incidence is higher in women and is more common in the fourth to fifth decades. Recurrences may be of either the diffuse type or the nodular type of episcleritis.
Codes
ICD10CM:
H15.129 – Nodular episcleritis, unspecified eye
SNOMEDCT:
70558001 – Nodular episcleritis
H15.129 – Nodular episcleritis, unspecified eye
SNOMEDCT:
70558001 – Nodular episcleritis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:03/11/2021
Last Updated:03/21/2021
Last Updated:03/21/2021