Epibulbar dermoid cyst - External and Internal Eye
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

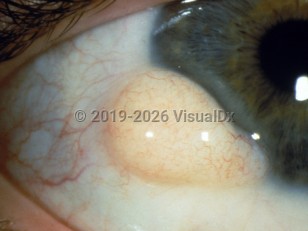
Dermoids are an overgrowth of normal, non-cancerous tissue in choristomatous tissue (tissue in an abnormal location). Epibulbar dermoid cysts are either limbal, at the junction of the cornea and sclera, or more posterior, at the junction of the bulbar and lid conjunctiva. Limbal epibulbar dermoid cysts are most often found at the inferior temporal limbus, while the posterior epibulbar dermoid cysts are often hidden under the outer upper eyelid laterally. Worldwide incidence is 1–3 per 10,000. These lesions may not only be cosmetically disfiguring but affect vision depending on how they affect the cornea and, hence, refractive status. Therefore, amblyopia is a serious concern with the limbal form. Foreign body sensation and an enlarging mass may also be presenting symptoms.
Codes
ICD10CM:
D31.00 – Benign neoplasm of unspecified conjunctiva
SNOMEDCT:
830036006 – Dermoid cyst of eye proper
D31.00 – Benign neoplasm of unspecified conjunctiva
SNOMEDCT:
830036006 – Dermoid cyst of eye proper
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:05/29/2007
Epibulbar dermoid cyst - External and Internal Eye