Emergency: requires immediate attention
Corneal chemical burn - External and Internal Eye
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

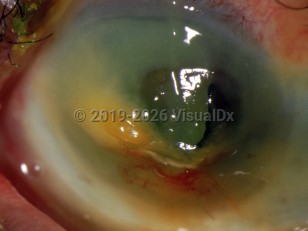
Corneal and conjunctival exposure to caustic material can be a devastating and painful ocular injury. The majority of the chemical injuries are due to basic compounds, but acid and solvent injuries are also seen. The amount of damage done to the cornea and ocular surface depends on the pH of the chemical, exposure time, and amount of exposure.
Chemical injuries are most commonly seen in young male individuals (often not using adequate eye protection) and in persons using bleach and other cleaning solutions. The injuries also occur when contact lens wearers mistake 3% hydrogen peroxide contact lens cleaning solution (eg, Clear Care), which cannot be used directly on the eye, with multipurpose rinsing and soaking solution, which can be used directly on the eye.
It is essential to initiate treatment for chemical injuries as soon as possible to minimize damage.
Patients with chemical injuries to the eye will often be in severe pain and not be able to open the affected eye(s). There will also be excessive tearing in the affected eye. In splash injuries, there are often associated chemical burns on the eyelid and face. Long-term sequelae such as corneal scarring and structural changes of the eyelid may occur.
Chemical injuries are most commonly seen in young male individuals (often not using adequate eye protection) and in persons using bleach and other cleaning solutions. The injuries also occur when contact lens wearers mistake 3% hydrogen peroxide contact lens cleaning solution (eg, Clear Care), which cannot be used directly on the eye, with multipurpose rinsing and soaking solution, which can be used directly on the eye.
It is essential to initiate treatment for chemical injuries as soon as possible to minimize damage.
Patients with chemical injuries to the eye will often be in severe pain and not be able to open the affected eye(s). There will also be excessive tearing in the affected eye. In splash injuries, there are often associated chemical burns on the eyelid and face. Long-term sequelae such as corneal scarring and structural changes of the eyelid may occur.
Codes
ICD10CM:
T26.60XA – Corrosion of cornea and conjunctival sac, unspecified eye, initial encounter
SNOMEDCT:
231945007 – Chemical injury to cornea
T26.60XA – Corrosion of cornea and conjunctival sac, unspecified eye, initial encounter
SNOMEDCT:
231945007 – Chemical injury to cornea
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:06/30/2019
Last Updated:07/01/2019
Last Updated:07/01/2019
Emergency: requires immediate attention
Corneal chemical burn - External and Internal Eye