Proptosis - External and Internal Eye
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

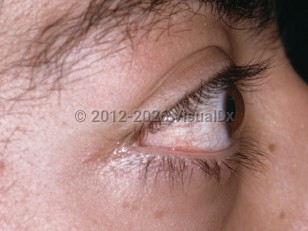
The direction in which the globe is displaced can help determine the likely etiology of proptosis. Retrobulbar lesions within the muscle cone, such as cavernous hemangioma, glioma, meningioma, hydatid cysts, metastases, and arteriovenous malformations, usually cause axial displacement of the globe. Maxillary sinus tumors cause superior displacement of the globe, while frontoethmoidal mucoceles, abscesses, osteomas, dermoid cysts, and lacrimal gland tumors cause inferior displacement.
Idiopathic orbital inflammation can mimic an orbital tumor by causing proptosis. It is most likely associated with underlying autoimmune pathology. It typically presents with unilateral proptosis and responds well to treatment with systemic corticosteroids.
Thyroid-related orbitopathy, another autoimmune disease, is the most common cause of both unilateral and bilateral proptosis in adults. White women between 30 and 50 years of age are most frequently affected. Here proptosis may be associated with eyelid retraction, abnormal thyroid levels, strabismus, and optic nerve compromise.
Codes
H05.20 – Unspecified exophthalmos
SNOMEDCT:
18265008 – Exophthalmos
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required