Felon - Nail and Distal Digit
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

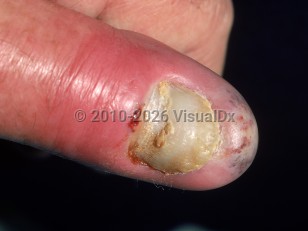
Felon is an acute infection of the fingertip pulp. Along with paronychias, they account for one-third of all hand infections. Cellulitis may lead to abscess formation, which occurs in the small, confined compartments of the fingertip pulp formed by vertical fibrous septa. The most common insult leading to felon is penetrating trauma with accompanying bacterial introduction, although untreated paronychia can also lead to felon. The thumb and index finger are most commonly involved. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common causative agent of felon.
Patients typically present with acute onset of pain, erythema, and edema at the distal fingertip pulp or pad. The distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint is the most proximal point of edema spread in felon. Containment of the abscess within the compartment can lead to high pressures at the fingertip and possible visible sinus formation. If blood flow is compromised, skin and pulp necrosis may ensue. Other complications include osteoarthritis, tenosynovitis, and septic arthritis.
Risk factors include any immunocompromised state, diabetes mellitus, and intravenous (IV) drug use, as well as work environments with increased risk of finger trauma. Immunocompromised patients have an increased risk of developing osteomyelitis. In addition, gram-negative organisms may be causative agents.
Patients typically present with acute onset of pain, erythema, and edema at the distal fingertip pulp or pad. The distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint is the most proximal point of edema spread in felon. Containment of the abscess within the compartment can lead to high pressures at the fingertip and possible visible sinus formation. If blood flow is compromised, skin and pulp necrosis may ensue. Other complications include osteoarthritis, tenosynovitis, and septic arthritis.
Risk factors include any immunocompromised state, diabetes mellitus, and intravenous (IV) drug use, as well as work environments with increased risk of finger trauma. Immunocompromised patients have an increased risk of developing osteomyelitis. In addition, gram-negative organisms may be causative agents.
Codes
ICD10CM:
L03.019 – Cellulitis of unspecified finger
SNOMEDCT:
32021005 – Felon
L03.019 – Cellulitis of unspecified finger
SNOMEDCT:
32021005 – Felon
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:06/07/2018
Last Updated:07/05/2018
Last Updated:07/05/2018
Felon - Nail and Distal Digit