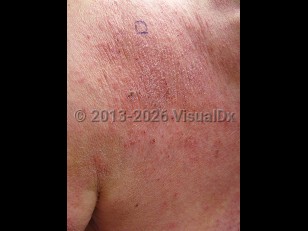
Chronic prescription drug use may be a common cause of CEEA. This is especially relevant in the aging population, as medication use increases with age. Retrospective case control studies have shown that calcium channel blockers and possibly hydrochlorothiazide are associated with CEEA more than other medication classes.
The case definition of CEEA includes the following:
- Age 50 or older
- At least 2 months duration of the eruption
- A symmetrical eczematous eruption (ie, pruritic, erythematous, scaly, subacute, or chronic dermatitis lesions) involving the trunk and extremities (with proclivity for extensor aspects of the extremities)
- Routine skin biopsy consistent with an eczematous eruption (the presence of spongiotic dermatitis in the inflammatory infiltrate and/or the presence of overlapping elements of other inflammatory histologic patterns)
- No prior history of an underlying dermatitis that would be compatible with the eruption (ie, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis)