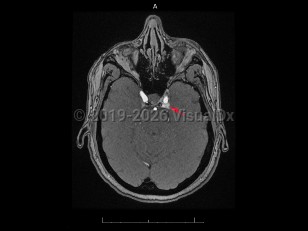
Carotid-cavernous fistula
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Acquired vascular abnormality involving communication between the cavernous sinus and the carotid artery or branches. It may arise spontaneously or through injury by blunt head trauma, surgery, or vascular and connective tissue disorders, or following cavernous carotid aneurysm rupture. Onset may be delayed. Carotid-cavernous fistula (CCF) are classified as high-flow (direct) or low-flow (indirect), depending on the pressure and direction of the communicating arterial blood flow. Common symptoms include bruit, proptosis, diplopia, blurred vision, visual loss, conjunctival injection, eye pain, headache, and chemosis. CCF affects men and women about equally. Rarely, they appear bilaterally.
Treatment depends on the classification of the CCF, with endovascular obliteration being the first approach to closure, although multiple procedures may be necessary.
Treatment depends on the classification of the CCF, with endovascular obliteration being the first approach to closure, although multiple procedures may be necessary.
Codes
ICD10CM:
I67.1 – Cerebral aneurysm, nonruptured
SNOMEDCT:
302213007 – Caroticocavernous sinus fistula
I67.1 – Cerebral aneurysm, nonruptured
SNOMEDCT:
302213007 – Caroticocavernous sinus fistula
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:01/14/2016
Carotid-cavernous fistula