Angiofibroma in Child
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Cutaneous angiofibroma is a term encompassing a range of skin lesions, including angiofibromas or "adenoma sebaceum" of tuberous sclerosis (TS), fibrous papules of the face, pearly penile papules, and acral fibrokeratomas.
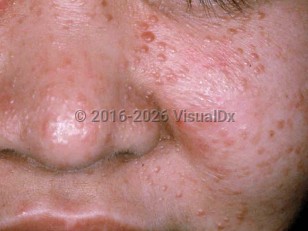
The angiofibromas of the face seen with TS consist of papules, nodules, and occasionally plaques in a butterfly distribution and in the nasolabial grooves in a symmetric pattern. These typically develop in childhood and adolescence and can be misdiagnosed as lesions of acne vulgaris. The fibrous cephalic plaque is a larger variant of an angiofibroma seen in up to 20% of TS patients, most often located on the forehead or scalp. Multiple facial angiofibromas can also be seen in other syndromes, including multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1), neurofibromatosis (NF) type 2, and Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome.
Fibrous papules of the face are usually solitary or few in number, most often seen in adults. They are dome shaped and skin colored, usually asymptomatic, with a predilection for the nose.
Pearly penile papules are chronic, asymptomatic, pinpoint (1-3 mm) white papules found in a circumferential distribution along the coronal margin and sulcus of the penis in up to 30% of adult males. They are observed more frequently in uncircumcised men.
Acral fibrokeratomas include acquired digital fibrokeratoma and periungual fibrokeratoma as well as the periungual, subungual, and ungual fibromas (Koenen tumors) of TS. Isolated lesions of acquired digital fibrokeratomas present as hyperkeratotic papules on the digits surrounded by a collarette of scale. Periungual fibromas are pink or skin colored and originate from the proximal nail fold, whereas subungual fibromas originate from underneath the nail plate.
The angiofibromas of the face seen with TS consist of papules, nodules, and occasionally plaques in a butterfly distribution and in the nasolabial grooves in a symmetric pattern. These typically develop in childhood and adolescence and can be misdiagnosed as lesions of acne vulgaris. The fibrous cephalic plaque is a larger variant of an angiofibroma seen in up to 20% of TS patients, most often located on the forehead or scalp. Multiple facial angiofibromas can also be seen in other syndromes, including multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1), neurofibromatosis (NF) type 2, and Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome.
Fibrous papules of the face are usually solitary or few in number, most often seen in adults. They are dome shaped and skin colored, usually asymptomatic, with a predilection for the nose.
Pearly penile papules are chronic, asymptomatic, pinpoint (1-3 mm) white papules found in a circumferential distribution along the coronal margin and sulcus of the penis in up to 30% of adult males. They are observed more frequently in uncircumcised men.
Acral fibrokeratomas include acquired digital fibrokeratoma and periungual fibrokeratoma as well as the periungual, subungual, and ungual fibromas (Koenen tumors) of TS. Isolated lesions of acquired digital fibrokeratomas present as hyperkeratotic papules on the digits surrounded by a collarette of scale. Periungual fibromas are pink or skin colored and originate from the proximal nail fold, whereas subungual fibromas originate from underneath the nail plate.
Codes
ICD10CM:
D36.9 – Benign neoplasm, unspecified site
SNOMEDCT:
302857002 – Angiofibroma
D36.9 – Benign neoplasm, unspecified site
SNOMEDCT:
302857002 – Angiofibroma
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:09/27/2018
Last Updated:10/25/2020
Last Updated:10/25/2020
Angiofibroma in Child