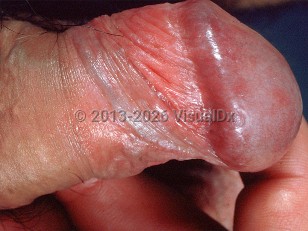
Bowenoid papulosis - Anogenital in
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Bowenoid papulosis (BP) is a clinical variant of a low-grade squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCCIS) caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), usually subtype 16, although other subtypes may occur. Smoking, early sexual initiation, multiple sexual partners, uncircumcised male sexual partners, and immunosuppression are contributory factors.
BP typically occurs in young sexually active adults. There is an equal male-to-female ratio. Lesions are usually asymptomatic, but may be itchy, and occur primarily in the genital and perianal region. The vulva is commonly involved.
BP has a variable course, with a frequent potential for spontaneous regression as well as persistence and recurrence. A postsurgical excision recurrence rate of up to 20.3% has also been documented.
The risk of progression to invasive SCC in immunocompetent patients is estimated at 2.6%. In immunocompromised patients, the risk of invasive malignancy, including cervical neoplasia, may be higher; one-half of HIV-infected patients with anogenital warts have SCCIS on histology.
In 2015, the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Diseases (ISSVD) recommended the term high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) to encompass all histopathologic diagnoses of vulvar precancer, and does not specifically delineate the clinical entity of BP. Many dermatology textbooks continue to include BP given its distinctive clinical appearance.
BP typically occurs in young sexually active adults. There is an equal male-to-female ratio. Lesions are usually asymptomatic, but may be itchy, and occur primarily in the genital and perianal region. The vulva is commonly involved.
BP has a variable course, with a frequent potential for spontaneous regression as well as persistence and recurrence. A postsurgical excision recurrence rate of up to 20.3% has also been documented.
The risk of progression to invasive SCC in immunocompetent patients is estimated at 2.6%. In immunocompromised patients, the risk of invasive malignancy, including cervical neoplasia, may be higher; one-half of HIV-infected patients with anogenital warts have SCCIS on histology.
In 2015, the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Diseases (ISSVD) recommended the term high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) to encompass all histopathologic diagnoses of vulvar precancer, and does not specifically delineate the clinical entity of BP. Many dermatology textbooks continue to include BP given its distinctive clinical appearance.
Codes
ICD10CM:
D04.9 – Carcinoma in situ of skin, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
402913004 – Bowenoid papulosis
D04.9 – Carcinoma in situ of skin, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
402913004 – Bowenoid papulosis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:08/11/2019
Last Updated:02/18/2020
Last Updated:02/18/2020
Bowenoid papulosis - Anogenital in