Choroidal nevus - External and Internal Eye
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Choroidal nevus is a common benign tumor found on the fundus. In population-based studies, the prevalence has ranged from 1.9% for patients older than 13 years to 6.5% for those older than 49. It is found predominantly in white individuals and has a small potential for growth into a melanoma.
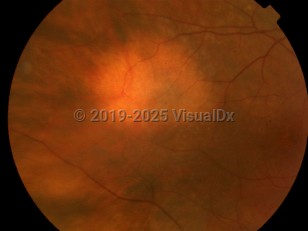
Though the tumor usually presents as a brown mass, the lesion can appear either pigmented or nonpigmented. The choroidal nevus is generally less than 2-mm thick, deep to the retina and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), and round or oval shaped. Drusen and other signs of retinal degeneration are commonly associated with choroidal nevi as well.
Vision loss, flashes of light, floaters, and visual field defects may be present in up to 14% of patients with choroidal nevi. Patients with a nevus at the fovea are at highest risk for vision loss.
In addition to the risk of vision loss due to choroidal nevus, there is a small but significant risk for transformation into melanoma. Less than 5% of "benign nevi" and 14% of "suspicious nevi" exhibit growth over 5 years. Published data of the US white population suggests a low rate (1 per 8845) of malignant transformation of a choroidal nevus.
Several reports have identified clinical risk factors for choroidal nevus transformation into melanoma, including thickness over 2 mm, subretinal fluid, symptoms, orange pigment, location near the optic disc, lack of overlying drusen, fluorescein angiographic hot spots over the tumor, and hollowness on ultrasonography.
Though the tumor usually presents as a brown mass, the lesion can appear either pigmented or nonpigmented. The choroidal nevus is generally less than 2-mm thick, deep to the retina and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), and round or oval shaped. Drusen and other signs of retinal degeneration are commonly associated with choroidal nevi as well.
Vision loss, flashes of light, floaters, and visual field defects may be present in up to 14% of patients with choroidal nevi. Patients with a nevus at the fovea are at highest risk for vision loss.
In addition to the risk of vision loss due to choroidal nevus, there is a small but significant risk for transformation into melanoma. Less than 5% of "benign nevi" and 14% of "suspicious nevi" exhibit growth over 5 years. Published data of the US white population suggests a low rate (1 per 8845) of malignant transformation of a choroidal nevus.
Several reports have identified clinical risk factors for choroidal nevus transformation into melanoma, including thickness over 2 mm, subretinal fluid, symptoms, orange pigment, location near the optic disc, lack of overlying drusen, fluorescein angiographic hot spots over the tumor, and hollowness on ultrasonography.
Codes
ICD10CM:
D31.30 – Benign neoplasm of unspecified choroid
SNOMEDCT:
255024002 – Nevus of choroid
D31.30 – Benign neoplasm of unspecified choroid
SNOMEDCT:
255024002 – Nevus of choroid
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:07/23/2013
Choroidal nevus - External and Internal Eye