Darier disease - Nail and Distal Digit
See also in: Overview,AnogenitalAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Darier disease, also known as keratosis follicularis or Darier-White disease, is an autosomal dominantly inherited disease caused by mutations in the ATP2A2 gene, which encodes a sarco / endoplasmic reticulum calcium-ATPase pump (SERCA2). Although disease penetrance is high, expression is variable, and sporadic mutations may occur. There is no sex predilection. Darier disease involves both abnormal keratinization and epidermal cell-to-cell adhesion.
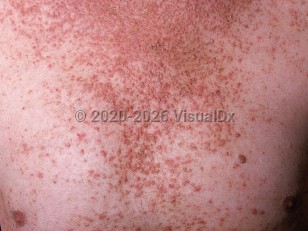
Dermatologic findings usually present in early adolescence to mid-adult life. Cutaneous findings include greasy hyperkeratotic papules in a seborrheic distribution, along with palmoplantar pits and acrokeratosis verruciformis-like papules. Leukodermic macules are a rarely reported finding. These small macules occur most frequently on the ventral aspects of the limbs and trunk.
In addition to cutaneous findings, 15%-50% of patients present with oral involvement, including cobblestoning of the oral mucosa, gingival hypertrophy, and sialadenitis. Esophageal involvement with erosions has been described. The severity of oral disease may parallel that of cutaneous disease.
Nail findings are seen in 92%-95% of patients with Darier disease. In addition, nails with multiple red and white bands resembling candy canes are pathognomonic for Darier disease. These findings may be accompanied by one or more V-shaped notches on the free edges of the nails. A wedge-shaped subungual keratosis may also be seen. Typically, 2 or 3 nails may be affected; rarely, all 20 nails may be involved. Toenails are affected less frequently than fingernails. There is rarely an association of twenty-nail dystrophy with Darier disease.
Dermatologic findings usually present in early adolescence to mid-adult life. Cutaneous findings include greasy hyperkeratotic papules in a seborrheic distribution, along with palmoplantar pits and acrokeratosis verruciformis-like papules. Leukodermic macules are a rarely reported finding. These small macules occur most frequently on the ventral aspects of the limbs and trunk.
In addition to cutaneous findings, 15%-50% of patients present with oral involvement, including cobblestoning of the oral mucosa, gingival hypertrophy, and sialadenitis. Esophageal involvement with erosions has been described. The severity of oral disease may parallel that of cutaneous disease.
Nail findings are seen in 92%-95% of patients with Darier disease. In addition, nails with multiple red and white bands resembling candy canes are pathognomonic for Darier disease. These findings may be accompanied by one or more V-shaped notches on the free edges of the nails. A wedge-shaped subungual keratosis may also be seen. Typically, 2 or 3 nails may be affected; rarely, all 20 nails may be involved. Toenails are affected less frequently than fingernails. There is rarely an association of twenty-nail dystrophy with Darier disease.
Codes
ICD10CM:
Q82.8 – Other specified congenital malformations of skin
SNOMEDCT:
48611009 – Darier's disease
Q82.8 – Other specified congenital malformations of skin
SNOMEDCT:
48611009 – Darier's disease
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:12/14/2025
Last Updated:09/13/2023
Last Updated:09/13/2023
Darier disease - Nail and Distal Digit
See also in: Overview,Anogenital