Lichen planus in Infant/Neonate
See also in: Anogenital,Nail and Distal DigitAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Childhood LP has been described after hepatitis B vaccination. Drugs causing LP-like eruptions (lichenoid drug reactions) include antihypertensives (ACE inhibitors: captopril and enalapril; beta blockers: propranolol and labetalol), thiazide diuretics, antimalarials (quinidine and hydroxychloroquine), penicillamine, NSAIDs, griseofulvin, tetracycline, antiepileptics, and many other drugs.
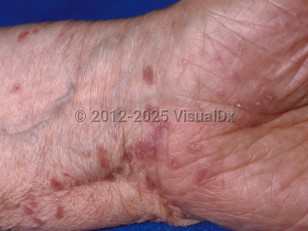
LP usually affects the glabrous (non-hair-bearing) skin and sometimes the mucosa, scalp, and nails. (See oral lichen planus for oral mucosal presentation and see lichen planopilaris for scalp presentation.) The frequency of childhood LP varies from 2.1%-11.2% of all cases of LP.
The majority of children who develop LP develop the classic form. Other variants include actinic, hypertrophic, linear, eruptive, follicular, atrophic, and bullous lesions.
LP may resolve spontaneously over several months. However, the disease generally has a chronic course with frequent remissions and exacerbations.
Codes
L43.9 – Lichen planus, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
4776004 – Lichen planus
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:05/06/2019
 Patient Information for Lichen planus in Infant/Neonate
Patient Information for Lichen planus in Infant/Neonate- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient