Puss caterpillar sting in Adult
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

There are more than 165 000 species of caterpillars worldwide, 150 of which are of medical importance. The most dangerous caterpillar in the United States is the puss caterpillar, Megalopyge opercularis, also known as the asp caterpillar.
The puss caterpillar is the larval form of the flannel moth that inhabits the southeastern United States and Latin America (also called tree asp, pussy moth, and southern flannel moth). The caterpillar is approximately 34 mm long and completely covered with long, brown, soft, woolly, urticating hairs that can cause dermatitis when touched or shortness of breath if inhaled. Hidden among the hairs are breakaway hollow spines that can inject venom, if touched, and induce a toxic dermatitis.
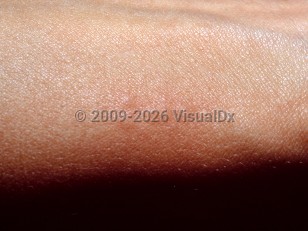
Contact with a puss caterpillar spine causes instant local pain that can be intense and radiating. Some report the sting as the worst pain ever experienced. Typically, the sting site develops localized erythema and swelling that may then evolve within 2-3 hours into a grid-like pattern of hemorrhagic papules. The dermatitis often lasts for a day or two. Systemic symptoms including nausea, vomiting, and lymphadenitis are often reported. Fever, muscles cramps, and seizure are occasionally reported; anaphylaxis is rare. Most stings occur late summer and early fall. Outbreaks of puss caterpillar stings can occur, often when the caterpillars fall from trees and come in contact with humans.
Puss caterpillar venom is poorly understood.
Related topic: caterpillar dermatitis
The puss caterpillar is the larval form of the flannel moth that inhabits the southeastern United States and Latin America (also called tree asp, pussy moth, and southern flannel moth). The caterpillar is approximately 34 mm long and completely covered with long, brown, soft, woolly, urticating hairs that can cause dermatitis when touched or shortness of breath if inhaled. Hidden among the hairs are breakaway hollow spines that can inject venom, if touched, and induce a toxic dermatitis.
Contact with a puss caterpillar spine causes instant local pain that can be intense and radiating. Some report the sting as the worst pain ever experienced. Typically, the sting site develops localized erythema and swelling that may then evolve within 2-3 hours into a grid-like pattern of hemorrhagic papules. The dermatitis often lasts for a day or two. Systemic symptoms including nausea, vomiting, and lymphadenitis are often reported. Fever, muscles cramps, and seizure are occasionally reported; anaphylaxis is rare. Most stings occur late summer and early fall. Outbreaks of puss caterpillar stings can occur, often when the caterpillars fall from trees and come in contact with humans.
Puss caterpillar venom is poorly understood.
Related topic: caterpillar dermatitis
Codes
ICD10CM:
T63.431A – Toxic effect of venom of caterpillars, accidental, initial encounter
SNOMEDCT:
16947009 – Poisoning by puss caterpillar
T63.431A – Toxic effect of venom of caterpillars, accidental, initial encounter
SNOMEDCT:
16947009 – Poisoning by puss caterpillar
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:07/05/2021
Puss caterpillar sting in Adult