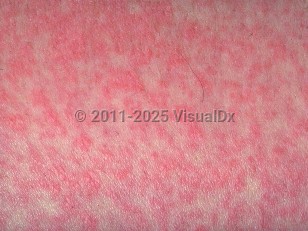
Viral exanthem in Infant/Neonate
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

The term "exanthem" is derived from the Greek "exanthema," which translates to "breaking out," and is used to describe cutaneous eruptions that arise abruptly and on several skin surfaces at once. In contrast, "enanthem" refers to mucous membrane involvement. Several viral infections are associated with viral exanthems and/or enanthems. Many of the cutaneous and mucosal findings of these infections are nonspecific in nature, but key aspects of the clinical history and presentation can suggest select etiologies.
During spring and winter, nonspecific eruptions can be seen with upper respiratory illnesses, often due to parainfluenza viruses, respiratory syncytial viruses, rhinovirus, and type A and B influenza virus. These are generally morbilliform in appearance and can last for several days. Petechial lesions can also be seen in influenza and enteroviral infections when generalized.
The congenital appearance of "blueberry muffin" skin lesions raises concern for the TORCH syndrome infections (Toxoplasma, other infections [such as HIV], rubella, cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex). Neonatal varicella syndrome presents 5-12 days postpartum as a hemorrhagic exanthem with multiorgan involvement leading to a 35% mortality rate.
The classic childhood diseases that cause viral exanthems were originally named numerically for the order in which they were discovered. Scarlet fever (second disease) is secondary to a bacterial infection and will not be covered in this section. Fourth disease is no longer felt to represent a distinct entity. Measles (rubeola, first disease) and rubella (third disease) have largely been prevented by vaccination in industrialized countries; however, suspicion must remain high given the recent trend toward refusing childhood vaccination and in the case of nonimmunized or underimmunized immigrants.
Measles occurs secondary to paramyxovirus. Among US-resident confirmed measles cases from 2009-2014, infants aged 6-11 months had the second highest incidence of cases after children aged 12-15 months. Classically, after 10-14 days, a prodrome of fever, dry cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis (often with photosensitivity) occurs, with development of Koplik spots (gray-white papules on the buccal mucosa) approximately 2 days prior to cutaneous symptoms. The exanthem begins on the head and proceeds in a cephalocaudal progression. Petechial, vesicular, and purpuric lesions have been described in association with atypical measles. The rash fades after about 5 days, also in a cephalocaudal fashion. Affected individuals are contagious for about 4 days prior to and after the exanthem.
Erythema infectiosum (fifth disease) occurs secondary to parvovirus B19. It is most commonly noted in patients aged 4-10 years.
Roseola (sixth disease, exanthem subitum) occurs secondary to human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 or HHV-7 and occurs in patients younger than age 2 years. A prodrome of high fever in an otherwise well child occurs for up to 5 days, followed by a sudden defervescence and appearance of rose-pink macules and papules with white halos (subitum is Latin for "suddenly"). The presence of this exanthem marks the end of viremia. Palpebral and periorbital edema (Berliner sign) may be seen.
Coxsackievirus can lead to herpangina in infants and children younger than 5 years. Following a brief incubation period, patients experience a sudden onset fever with malaise, headache, and myalgias. Oral lesions comprising 1- to 2-mm gray-white papulovesicles progress to ulcerations surrounded by an erythematous rim on the anterior tonsillar pillars, soft palate, uvula, and tonsils, as well as diffuse pharyngeal hyperemia. There is no associated cutaneous exanthem. Oral lesions resolve after 1 week.
Hemangioma-like lesions (erythematous papules with central pinpoint vascular supply and surrounding avascular halo) have been reported in infants aged 8-11 months in association with echovirus infections. This exanthem has been coined eruption pseudoangiomatosis.
Exanthems and/or enanthems have been reported with COVID-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. See skin and oral mucosal manifestations of COVID-19 for further details.
The presence of localized lesions raises suspicion for unilateral laterothoracic exanthem, which affects children aged 6 months to 10 years. Lesions arise unilaterally around the axillary vault or inguinal crease before progressing to demonstrate bilateral involvement. Lesions are initially papular but progress to an eczematous appearance. Cutaneous lesions resolve over a period of weeks to months.
During spring and winter, nonspecific eruptions can be seen with upper respiratory illnesses, often due to parainfluenza viruses, respiratory syncytial viruses, rhinovirus, and type A and B influenza virus. These are generally morbilliform in appearance and can last for several days. Petechial lesions can also be seen in influenza and enteroviral infections when generalized.
The congenital appearance of "blueberry muffin" skin lesions raises concern for the TORCH syndrome infections (Toxoplasma, other infections [such as HIV], rubella, cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex). Neonatal varicella syndrome presents 5-12 days postpartum as a hemorrhagic exanthem with multiorgan involvement leading to a 35% mortality rate.
The classic childhood diseases that cause viral exanthems were originally named numerically for the order in which they were discovered. Scarlet fever (second disease) is secondary to a bacterial infection and will not be covered in this section. Fourth disease is no longer felt to represent a distinct entity. Measles (rubeola, first disease) and rubella (third disease) have largely been prevented by vaccination in industrialized countries; however, suspicion must remain high given the recent trend toward refusing childhood vaccination and in the case of nonimmunized or underimmunized immigrants.
Measles occurs secondary to paramyxovirus. Among US-resident confirmed measles cases from 2009-2014, infants aged 6-11 months had the second highest incidence of cases after children aged 12-15 months. Classically, after 10-14 days, a prodrome of fever, dry cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis (often with photosensitivity) occurs, with development of Koplik spots (gray-white papules on the buccal mucosa) approximately 2 days prior to cutaneous symptoms. The exanthem begins on the head and proceeds in a cephalocaudal progression. Petechial, vesicular, and purpuric lesions have been described in association with atypical measles. The rash fades after about 5 days, also in a cephalocaudal fashion. Affected individuals are contagious for about 4 days prior to and after the exanthem.
Erythema infectiosum (fifth disease) occurs secondary to parvovirus B19. It is most commonly noted in patients aged 4-10 years.
Roseola (sixth disease, exanthem subitum) occurs secondary to human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 or HHV-7 and occurs in patients younger than age 2 years. A prodrome of high fever in an otherwise well child occurs for up to 5 days, followed by a sudden defervescence and appearance of rose-pink macules and papules with white halos (subitum is Latin for "suddenly"). The presence of this exanthem marks the end of viremia. Palpebral and periorbital edema (Berliner sign) may be seen.
Coxsackievirus can lead to herpangina in infants and children younger than 5 years. Following a brief incubation period, patients experience a sudden onset fever with malaise, headache, and myalgias. Oral lesions comprising 1- to 2-mm gray-white papulovesicles progress to ulcerations surrounded by an erythematous rim on the anterior tonsillar pillars, soft palate, uvula, and tonsils, as well as diffuse pharyngeal hyperemia. There is no associated cutaneous exanthem. Oral lesions resolve after 1 week.
Hemangioma-like lesions (erythematous papules with central pinpoint vascular supply and surrounding avascular halo) have been reported in infants aged 8-11 months in association with echovirus infections. This exanthem has been coined eruption pseudoangiomatosis.
Exanthems and/or enanthems have been reported with COVID-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. See skin and oral mucosal manifestations of COVID-19 for further details.
The presence of localized lesions raises suspicion for unilateral laterothoracic exanthem, which affects children aged 6 months to 10 years. Lesions arise unilaterally around the axillary vault or inguinal crease before progressing to demonstrate bilateral involvement. Lesions are initially papular but progress to an eczematous appearance. Cutaneous lesions resolve over a period of weeks to months.
Codes
ICD10CM:
B09 – Unspecified viral infection characterized by skin and mucous membrane lesions
SNOMEDCT:
49882001 – Viral exanthem
B09 – Unspecified viral infection characterized by skin and mucous membrane lesions
SNOMEDCT:
49882001 – Viral exanthem
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:04/22/2025
Last Updated:05/19/2025
Last Updated:05/19/2025
 Patient Information for Viral exanthem in Infant/Neonate
Patient Information for Viral exanthem in Infant/Neonate
Premium Feature
VisualDx Patient Handouts
Available in the Elite package
- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient
Upgrade Today

Viral exanthem in Infant/Neonate