Cornelia de Lange syndrome in Child
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Cornelia de Lange syndrome is a clinically variable malformation disorder with widespread manifestations. The facial morphology is said to be distinctive in most individuals, characterized by arched or joined, bushy eyebrows (synophrys); long, thick eyelashes; a short, upturned nose with a broad bridge; diastema (gap between two teeth); and sometimes microbrachycephaly. Mild ptosis is common, and many patients have strabismus, myopia, and nystagmus. Hirsutism with a low hairline is present in the majority of individuals. The lips appear thin, and the mouth opening is crescent shaped. The ears are often low set and rotated posteriorly. The neck may be short, and the hard palate is highly arched and sometimes clefted. Infants with the more severe form often have a characteristic low-pitched cry that disappears in late infancy.
Growth retardation begins prenatally and is present throughout life. Mental development is also delayed in the majority of individuals, and some but not all have intellectual disabilities. The average intelligence quotient (IQ) is about 53. Seizures occur in about 1 in 4 individuals. Many patients are shy, with few social skills; patients sometimes have behavioral features of autism spectrum disorders. Middle ear infections are frequent and may result in a conductive hearing loss, while other patients have neurosensory hearing loss.
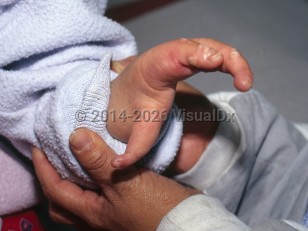
Limb and digital anomalies are common and may be asymmetric. These anomalies most commonly involve the upper limbs, which may be absent or severely reduced. Radioulnar fusion is an important sign. Digits are sometimes missing, but metacarpophalangeal malformations are more common. A shortened first metacarpal results in a proximally positioned thumb. A hypoplastic middle phalanx of the index finger is characteristic but not always present.
Cryptorchidism and hypoplastic genitalia are often present. Urinary infections have been reported in over 40% of patients. Cardiac septal defects and some degree of gastrointestinal dysfunction such as gastric reflux are common.
Growth retardation begins prenatally and is present throughout life. Mental development is also delayed in the majority of individuals, and some but not all have intellectual disabilities. The average intelligence quotient (IQ) is about 53. Seizures occur in about 1 in 4 individuals. Many patients are shy, with few social skills; patients sometimes have behavioral features of autism spectrum disorders. Middle ear infections are frequent and may result in a conductive hearing loss, while other patients have neurosensory hearing loss.
Limb and digital anomalies are common and may be asymmetric. These anomalies most commonly involve the upper limbs, which may be absent or severely reduced. Radioulnar fusion is an important sign. Digits are sometimes missing, but metacarpophalangeal malformations are more common. A shortened first metacarpal results in a proximally positioned thumb. A hypoplastic middle phalanx of the index finger is characteristic but not always present.
Cryptorchidism and hypoplastic genitalia are often present. Urinary infections have been reported in over 40% of patients. Cardiac septal defects and some degree of gastrointestinal dysfunction such as gastric reflux are common.
Codes
ICD10CM:
Q87.19 – Other congenital malformation syndromes predominantly associated with short stature
SNOMEDCT:
40354009 – De Lange syndrome
Q87.19 – Other congenital malformation syndromes predominantly associated with short stature
SNOMEDCT:
40354009 – De Lange syndrome
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:08/06/2023
Cornelia de Lange syndrome in Child